
^ "Stedman's Online | Reference" (PDF).^ The AAMT Book of Style for Medical Transcription, 2nd Ed., Peg Hughes, CMT, American Association for Medical Transcription, ISBN 0-93, copyright 2002.^ Vera Pyle’s Current Medical Terminology, 11th Ed., Health Professions Institute, Modesto, California, 2007, p.Acronym and initialism#Orthographic styling.Abbreviation#Style conventions in English.List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes.List of abbreviations used in medical prescriptions.Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrationīillionth of a gram also known as millimicrogramīillionth of a meter also known as millimicronĪlso referred to as nanometers/nanometres Required in some regions to avoid the confusion of 'μ' with 'm' ('milli-'). Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Often incorrectly used for bipolar disorder (BPAD is preferred)Ĭenters for Disease Control and PreventionĬreatine phosphokinase muscle bandisoenzymeĭiphtheria-tetanus-pertussis(toxoids/vaccine)Įndoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography This list uses significant capitalization for headwords (the abbreviations) and their expansions.

It generally uses the singular form of an abbreviation (not the plural) as the headword.It uses periods for certain abbreviations that traditionally often have them (mostly older Latin/Neo-Latin abbreviations).
#Dair medical abbreviation series
This series of lists omits periods from acronyms and initialisms. Some initialisms deriving from Latin may be pronounced either as letters ( qid = "cue eye dee") or using the English expansion ( qid = "four times a day"). Abbreviations of weights and measures are pronounced using the expansion of the unit ( mg = "milligram") and chemical symbols using the chemical expansion ( NaCl = "sodium chloride"). Pronunciation follows convention outside the medical field, in which acronyms are generally pronounced as if they were a word ( JAMA, SIDS), initialisms are generally pronounced as individual letters ( DNA, SSRI), and abbreviations generally use the expansion ( soln. The effect of BP on MI risk is multifaceted.Īrrows may be used to indicate numerous conditions including elevation (↑), diminution (↓), and causation (→, ←). BP's effect on risk of MI is multifaceted. Often the writer can also recast the sentence to avoid it. Possessive forms are not often needed, but can be formed using apostrophe + s. The prevalent way to represent plurals for medical acronyms and initialisms is simply to affix a lowercase s (no apostrophe). Less common: The diagnosis was C.O.P.D. Prevalent practice in medicine today is often to forgo them as unnecessary. Periods (stops) are often used in styling abbreviations. Certain medical abbreviations are avoided to prevent mistakes, according to best practices (and in some cases regulatory requirements) these are flagged in the list of abbreviations used in medical prescriptions. The advantages of brevity should be weighed against the possibilities of obfuscation (making the communication harder for others to understand) and ambiguity (having more than one possible interpretation). They boost efficiency as long as they are used intelligently. Abbreviations for diseases and disordersĪbbreviations are used very frequently in medicine. Abbreviations for medical organisations and personnel. DAIR - Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention. MHRA 'DAIR - Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention', All Acronyms,, Bluebook All Acronyms, DAIR - Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention (May. "DAIR - Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention". DAIR - Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention, All Acronyms, viewed May 30, 2023, MLA All Acronyms. 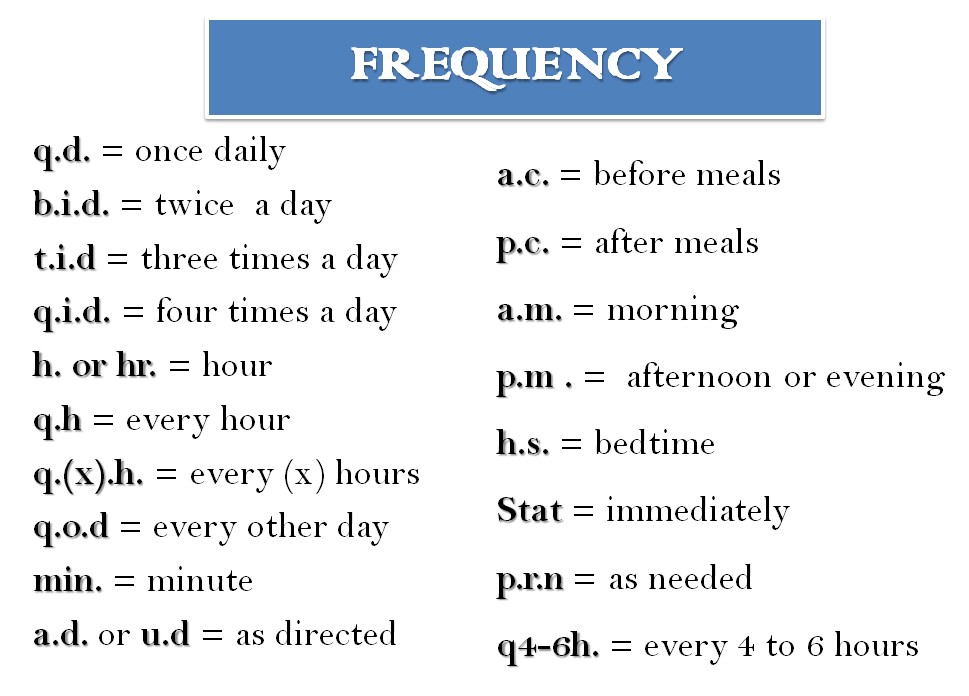
Retrieved May 30, 2023, from Chicago All Acronyms. Please use the following to spread the word:ĪPA All Acronyms.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
